Constipation, a common gastrointestinal issue, has been a subject of growing interest due to its potential connection to Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
Understanding this link is crucial not only for addressing specific health concerns but also for comprehending the broader impact on overall well-being.
In this article, we will answer the question, “can constipation cause ED?” and explore the potential association between erectile dysfunction and constipation to encourage a holistic approach to health and foster awareness about the intricate connections between various bodily functions.
Link between constipation and ED:
Erectile Dysfunction and constipation may seem unrelated, but recent research suggests a potential link, emphasizing the importance of understanding how chronic constipation can impact overall male sexual health.
Chronic Constipation’s Impact on the Body: Chronic constipation, characterized by infrequent and difficult bowel movements, can lead to a range of physical issues. Straining during bowel movements may cause increased pressure in the pelvic region, potentially affecting the nerves and blood vessels associated with sexual function.
Blood Flow and Nerve Function in ED: Erectile function relies heavily on proper blood flow and nerve function. Chronic constipation may contribute to compromised blood circulation in the pelvic area, impacting the ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Additionally, the nerves controlling sexual response may be affected due to prolonged strain during bowel movements.
How Does Constipation Impact Blood Flow to the Pelvic Region?
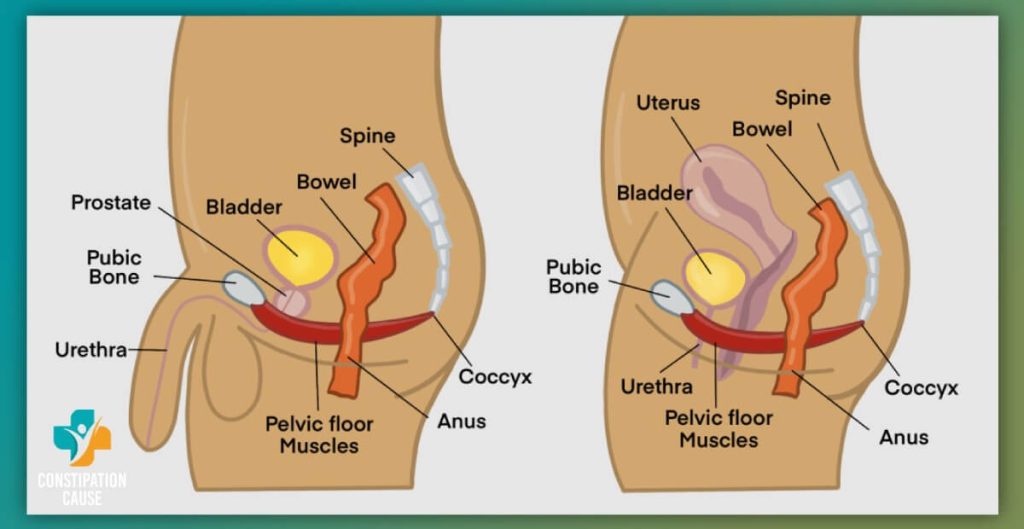
Chronic constipation can influence blood flow to the pelvic region through several physiological processes, potentially contributing to Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
1. Increased Intra-Abdominal Pressure:
Straining during constipation elevates intra-abdominal pressure, affecting the blood vessels supplying the pelvic organs, including those involved in sexual function.
2. Compression of Blood Vessels:
Prolonged straining may compress blood vessels in the pelvic area, restricting the smooth flow of blood to the penis. This compression can compromise vascular integrity over time.
3. Nerve Compression:
The pressure exerted during constipation may also affect the nerves responsible for sexual function. Compression of these nerves can disrupt the signaling required for a proper erectile response.
4. Impact on Hemorrhoidal Veins:
Chronic constipation is often associated with the development of hemorrhoids. These swollen veins in the rectum can impede blood flow and contribute to vascular dysfunction in the pelvic region.
Consequences of Reduced Blood Flow:
Reduced blood flow to the pelvic region can have significant consequences for erectile function:
1. Impaired Vasodilation:
Inadequate blood flow hinders the normal vasodilation required for the penis to fill with blood during arousal, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection.
2. Tissue Damage and Fibrosis:
Prolonged restriction of blood supply can lead to tissue damage and fibrosis in the erectile tissues, further compromising the ability to achieve and sustain a healthy erection.
3. Reduced Nitric Oxide Production:
Insufficient blood flow may impact the production of nitric oxide, a crucial chemical that facilitates the relaxation of blood vessels and supports normal erectile function.
The Nervous System and Erectile Dysfunction:
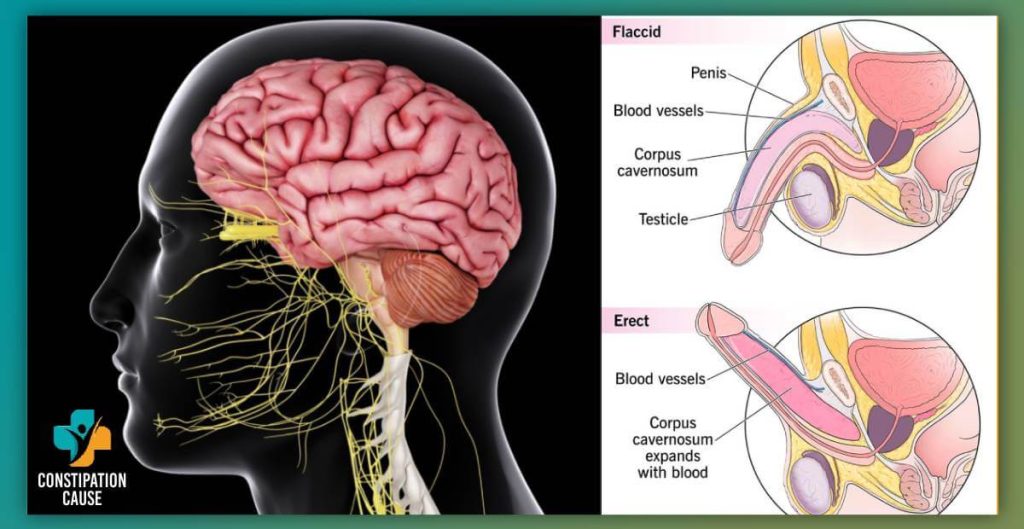
The nervous system plays a pivotal role in both gastrointestinal issues and erectile problems, revealing an intriguing connection between these seemingly disparate conditions.
1. Shared Autonomic Nervous System:
Both constipation and ED involve the autonomic nervous system, responsible for involuntary bodily functions. Disruptions in this system can affect various processes, including those related to the gastrointestinal and reproductive systems.
2. Straining and Nerve Compression:
Constipation often involves straining during bowel movements, leading to increased pressure on the pelvic nerves. Prolonged straining may result in nerve compression, impacting the intricate network that governs sexual response and function.
3. Sacral Nerves and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction:
The sacral nerves, located in the lower spine, play a crucial role in bowel and bladder function as well as sexual response. Constipation-induced strain can contribute to pelvic floor dysfunction, affecting the sacral nerves and potentially influencing erectile function.
4. Vagus Nerve and Gastrointestinal Impact:
The vagus nerve, a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system, connects the brain to the gut. Constipation-related issues may disrupt the communication between the brain and the digestive system through the vagus nerve, influencing both gastrointestinal and sexual functions.
5. Psychological Impact:
Chronic constipation can contribute to psychological stress, which in turn can affect the central nervous system. Stress and anxiety, common in constipation, are known contributors to ED, further emphasizing the interconnected nature of these conditions.
Disruption of Nerve Signals in Constipation and ED:
Constipation may disrupt nerve signals crucial for maintaining sexual function in several ways:
1. Altered Reflexes:
Straining during constipation can alter reflexes in the pelvic nerves, potentially affecting the coordination required for normal sexual response.
2. Nerve Compression and Dysfunction:
Prolonged compression of nerves due to constipation-induced pressure may lead to dysfunction, disrupting the intricate signaling required for optimal erectile function.
3. Central and Peripheral Nervous System Interplay:
The interplay between the central and peripheral nervous systems is intricate. Constipation-induced disruptions may influence both systems, impacting the regulation of sexual function.
Lifestyle Factors and Constipation-ED Connection:
Lifestyle factors, encompassing diet and physical activity, play a significant role in the intricate relationship between constipation and Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
1. Dietary Impact on Constipation:
Inadequate fiber intake, common in diets rich in processed foods, can contribute to constipation. A diet lacking in essential nutrients may affect digestive health, potentially influencing ED.
2. Dehydration and Gastrointestinal Function:
Insufficient fluid intake can lead to dehydration, contributing to constipation. Proper hydration is crucial for digestive health, and dehydration may indirectly affect ED by impacting blood flow.
3. Sedentary Lifestyle and Bowel Function:
Lack of physical activity is associated with slower bowel transit times, potentially leading to constipation. Regular exercise promotes healthy bowel movements and supports overall vascular health, crucial for ED prevention.
4. Obesity and Increased ED Risk:
Obesity, often linked to poor dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles, is a known risk factor for both constipation and ED. Excess weight can contribute to hormonal imbalances and vascular issues, affecting sexual function.
5. Psychosocial Factors:
Stress and anxiety, common in sedentary and high-stress lifestyles, can exacerbate both constipation and ED. Managing stress through lifestyle changes and relaxation techniques may positively impact both conditions.
Recommendations for Managing Constipation to Reduce ED Risk:
1. Balanced Diet with Adequate Fiber:
Prioritize a diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to promote regular bowel movements and support digestive health.
2. Hydration:
Ensure sufficient water intake throughout the day to prevent dehydration and maintain optimal bowel function.
3. Regular Physical Activity:
Incorporate regular exercise into your routine, focusing on activities that promote overall cardiovascular health and support healthy bowel movements.
4. Weight Management:
Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, reducing the risk of obesity-related complications that can contribute to both constipation and ED.
5. Mind-Body Practices:
Explore stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to alleviate psychosocial factors that may contribute to both constipation and ED.
Medical Conditions, Medications, and Their Impact:
Underlying medical conditions and medications can intertwine, contributing to both constipation and Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
1. Neurological Disorders:
Conditions like Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis may affect nerves controlling bowel and sexual function, leading to constipation and ED.
2. Endocrine Disorders:
Hormonal imbalances, as seen in diabetes or hypothyroidism, can impact both gastrointestinal motility and sexual function.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders:
Inflammatory bowel diseases, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or chronic intestinal infections can contribute to constipation and, indirectly, ED.
4. Psychiatric Medications:
Certain antidepressants and antipsychotics may have side effects, including constipation and ED, due to their impact on neurotransmitters and blood flow.
5. Antihypertensive Medications:
Some blood pressure medications, particularly diuretics and beta-blockers, may contribute to constipation and ED by affecting blood circulation.
Strategies for Preventing Constipation and ED:
- High-Fiber Diet: Prioritize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to promote regular bowel movements and support digestive health.
- Adequate Hydration: Ensure sufficient water intake throughout the day to prevent dehydration and maintain optimal bowel function.
- Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate regular exercise, focusing on activities that promote overall cardiovascular health and support healthy bowel movements.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, reducing the risk of obesity-related complications that can contribute to both constipation and ED.
- Mind-Body Practices: Explore stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to alleviate psychosocial factors that may contribute to both constipation and ED.
- Medication Review: Regularly review medications with healthcare professionals to assess side effects and explore potential adjustments or alternatives to minimize constipation and ED risks.
- Comprehensive Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical examination to identify and manage underlying health conditions contributing to constipation and ED.
- Collaborative Healthcare Team: Engage with a collaborative healthcare team, including gastroenterologists, urologists, and endocrinologists, to develop a comprehensive care plan addressing both conditions.
- Holistic Lifestyle Approach: Adopt a holistic approach to health that encompasses balanced nutrition, hydration, physical activity, and stress management to promote overall well-being and reduce the risk of constipation and ED.
Natural Remedies for Constipation and ED:
Impact of constipation on erectile function can be minimized by following these natural remedies:
1. Dietary Fiber: Increase fiber intake with whole foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains to promote healthy digestion and regular bowel movements.
2. Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day to support bowel function and maintain overall health.
3. Probiotics: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables to promote a healthy gut microbiome, potentially aiding in digestion.
4. Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, including aerobic activities and pelvic floor exercises, to support bowel regularity and enhance overall cardiovascular health.
5. Herbal Teas: Consider herbal teas such as peppermint or ginger, known for their digestive benefits, to help alleviate constipation.
6. Magnesium-Rich Foods: Include magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds in your diet, as magnesium may help relax muscles and support bowel movements.
7. Avoiding Triggers: Identify and limit intake of potential constipation triggers like processed foods, dairy, and excessive amounts of red meat.
8. Mind-Body Practices: Practice stress-reducing activities like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, which may positively impact both constipation and ED.
9. Acupuncture: Explore acupuncture as a complementary therapy; some studies suggest it may help alleviate constipation and improve sexual function.
10. Aromatherapy: Consider aromatherapy with essential oils like peppermint or lavender, as inhaling these scents may have relaxing effects on the gastrointestinal and nervous systems.
11. L-Arginine-Rich Foods: Include foods rich in L-arginine, such as nuts, seeds, and legumes, as this amino acid may help improve blood flow and support erectile function.
12. Gingko Biloba: Gingko biloba, an herbal supplement, has been studied for its potential benefits in improving blood flow and may have positive effects on ED.
13. Lifestyle Changes: Adopt overall lifestyle changes, including improved sleep, reduced alcohol intake, and smoking cessation, as these factors can positively impact both constipation and ED.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this article has elucidated the intricate connection between constipation and Erectile Dysfunction (ED), emphasizing the role of lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and medications in influencing both conditions. Recognizing the shared mechanisms and addressing them through dietary changes, regular exercise, and natural remedies may offer a holistic approach to managing constipation and potentially reducing the risk of ED. Understanding this interplay is essential for fostering overall health and well-being. It is strongly advised that readers consult with healthcare professionals if they have concerns about constipation, ED, or their potential correlation. Seeking timely medical advice ensures a tailored and comprehensive approach to address these conditions, promoting optimal digestive and sexual health.
I hope this article answer your question, “can constipation cause ED?”
Frequently Asked Questions
Can occasional constipation lead to ED?
Occasional constipation is unlikely to directly cause ED, but chronic constipation may contribute to factors affecting sexual function over time.
What are the common symptoms of ED?
Common symptoms of ED include difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, reduced sexual desire, and performance anxiety.
Are there specific foods that can help alleviate constipation and ED?
High-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can aid constipation, while foods rich in L-arginine, such as nuts and seeds, may support erectile function.
Can constipation cause temporary or long-term ED?
Prolonged or severe constipation may contribute to long-term ED by affecting blood flow and nerve function in the pelvic region.
What is the role of stress in both constipation and ED?
Stress can exacerbate both constipation and ED by influencing hormonal balance, nervous system function, and overall well-being.
How can I differentiate between constipation-related ED and other causes of ED?
Distinguishing between constipation-related ED and other causes involves assessing factors such as bowel habits, overall health, and the presence of chronic constipation symptoms.









Leave feedback about this