In recent years, almond milk has surged in popularity as a sought-after dairy alternative, celebrated for its creamy texture and nutty flavor. As more individuals now prefer plant-based lifestyles, the conversation has expanded beyond its nutritional merits to its potential impact on digestive health.
In this article, we will answer in detail, “will almond milk cause constipation?” and talk about Almond milk related constipation symptoms.
So, let’s get started!
What is Almond Milk?
Almond milk, a dairy-free beverage, is a product of blending almonds with water and straining the mixture to achieve a smooth, creamy liquid. The basic recipe includes almonds, water, and sometimes sweeteners or flavorings, providing a versatile and lactose-free alternative to traditional dairy milk. The almonds are typically soaked, blended, and then strained to extract the liquid, leaving behind almond solids. This process results in a beverage with a light, nutty flavor and a texture similar to that of cow’s milk.
Ingredients:
- Almonds: Packed with nutrients, almonds contribute a rich, nutty taste and provide essential vitamins and minerals.
- Water: The primary component for achieving the liquid consistency of almond milk.
- Sweeteners or Flavorings (optional): Some commercially available almond milks may include sweeteners like sugar or natural sweeteners, along with flavorings such as vanilla or chocolate.
Production Process:
- Soaking: Almonds are often soaked in water to soften them, making it easier to blend and extract flavors.
- Blending: The soaked almonds are blended with water to create a smooth, homogeneous mixture.
- Straining: The blended mixture is strained to separate the liquid from the almond solids, resulting in a milk-like liquid.
Almond milk has gained immense popularity among individuals with dietary restrictions, especially those following vegan, lactose-free, or plant-based diets.
Nutritional Profile of Almond Milk:
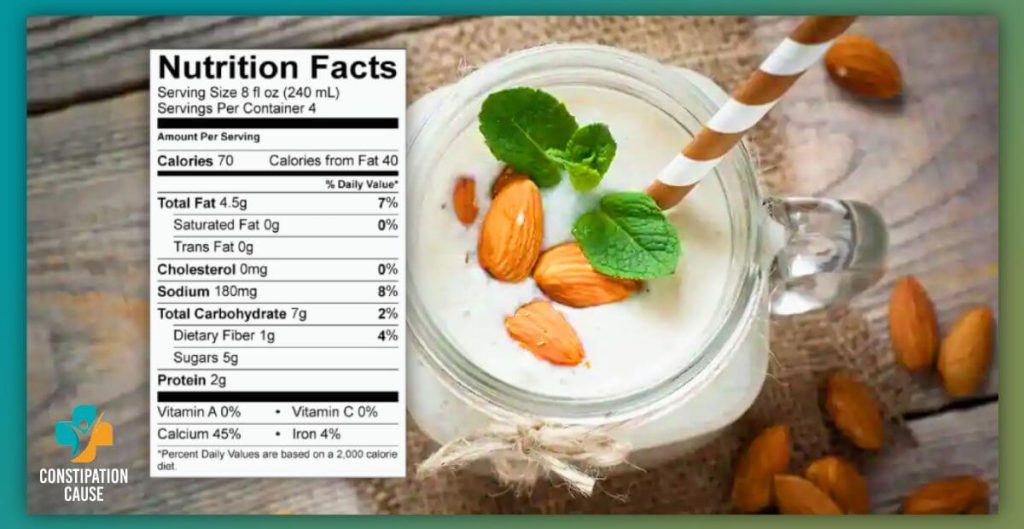
Almond milk, touted for its dairy-free appeal, offers a distinctive nutritional profile that distinguishes it from traditional cow’s milk. Understanding the key components of almond milk is essential for those seeking a plant-based alternative with specific dietary goals.
Caloric Content and Macronutrients: Almond milk is generally lower in calories compared to cow’s milk, making it a favorable option for those mindful of their caloric intake. A typical serving of unsweetened almond milk contains around 30 to 50 calories, making it a lighter alternative. In terms of macronutrients, almond milk is often lower in protein than cow’s milk but can be fortified to provide a comparable amount.
Healthy Fats: Almond milk is celebrated for its heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, contributing to a well-rounded lipid profile. These fats are known for their potential benefits in supporting cardiovascular health, making almond milk an appealing choice for those looking to incorporate more heart-friendly fats into their diet.
Fortification and Vitamins: Almond milk is frequently fortified with essential vitamins such as Vitamin D and Vitamin B12, addressing potential nutritional gaps in a plant-based diet. While cow’s milk is a natural source of these vitamins, fortified almond milk aims to provide a comparable nutritional offering for those who opt for a dairy-free lifestyle.
Calcium and Comparison to Cow’s Milk: One notable difference lies in the calcium content. While cow’s milk is a robust source of naturally occurring calcium, almond milk may be lower in this mineral. However, many commercially available almond milks are fortified with calcium to align more closely with the nutritional benefits of cow’s milk.
Now, let’s talk about Almond milk causing constipation:
The Connection between Almond Milk and Digestion
The General Link between Food/Drink and Digestive Health: Digestive health is closely intertwined with the composition of our diet. A diet rich in fiber, water, and nutrients generally supports optimal digestion, promoting regular bowel movements and overall gut health. Conversely, the overconsumption of certain ingredients, such as processed foods low in fiber, may contribute to digestive discomfort and constipation. Recognizing this interplay allows us to make informed choices for a digestive-friendly diet. Delving into specifics, explore the potential effects of skim milk on constipation for a nuanced perspective on your dietary choices.
Why does almond milk make me constipated?
Almond milk, often lauded for its nutritional benefits, has occasionally been associated with constipation due to its lower fiber content compared to whole almonds. While almonds themselves are a good source of fiber, the straining process during almond milk production may reduce the fiber content. Some individuals may experience changes in bowel habits when transitioning to almond milk, prompting common beliefs about its potential role in constipation.
Debunking the Almond Milk and Constipation Myth:
Almond milk, celebrated for its versatility and nutritional benefits, has found itself entangled in a common myth regarding its potential to cause constipation
One prevailing myth suggests almond milk causing constipation. This belief often stems from the assumption that the straining process during almond milk production removes fiber, a vital component for digestive regularity. However, this oversimplified view neglects the broader context of dietary choices, individual sensitivities, and the potential role of various factors in constipation.
Importance of Evidence-Based Information:
Understanding the impact of almond milk on digestion requires a more nuanced approach, considering the entire diet and individual differences. Evidence-based information is crucial in dispelling myths and providing a comprehensive understanding of how almond milk fits into a digestive-friendly lifestyle. Scientific studies and nutritional analyses help unveil the actual nutritional composition of almond milk, allowing consumers to make informed decisions based on facts rather than unfounded beliefs.
Contrary to the myth, almond milk can be part of a digestive-friendly diet. While it may be lower in fiber compared to whole almonds, many commercially available almond milks are fortified with nutrients like calcium and vitamins, contributing to overall nutritional well-being. Understanding that constipation is a multifaceted issue influenced by various factors underscores the importance of a holistic approach to digestive health.
The Benefits and Risks of Almond Milk for Digestion:

Benefits:
- Dietary Versatility: Almond milk offers a plant-based, lactose-free alternative suitable for various dietary preferences.
- Heart-Healthy Fats: Rich in monounsaturated fats, almond milk may support cardiovascular health.
- Fortification: Often fortified with essential nutrients like calcium and vitamins, contributing to overall nutritional intake.
- Hydration: A hydrating option that can complement a well-balanced diet.
Risks:
- Lower Fiber Content: Compared to whole almonds, almond milk may be lower in fiber, potentially affecting digestive regularity.
- Added Ingredients: Sweeteners or flavorings in some commercial varieties may impact the overall nutritional profile.
- Individual Sensitivities: Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort due to personal sensitivities to almonds or additives.
Can too much almond milk cause constipation?
Yes, too much consumption of Almond milk may cause constipation. Here a few recommendations:
Recommendations for Consumption:
- Moderation is Key: Enjoy almond milk in moderation, incorporating it into a balanced diet without overreliance.
- Consider Fiber Intake: Pair almond milk with fiber-rich foods to enhance its contribution to digestive regularity.
- Monitor Sweeteners: Opt for unsweetened varieties to avoid excess sugars, which may impact digestion.
Balancing Enjoyment and Digestive Wellness:
- Diverse Diet Inclusion: Balance almond milk consumption with a variety of foods, ensuring a well-rounded nutritional intake.
- Individual Sensitivity: Be mindful of personal sensitivities to almonds or additives, adjusting consumption accordingly.
Dosage Recommendations for Almond Milk Consumption:
- Portion Sizes: A serving size of almond milk is typically one cup (240 ml), providing nutrients without overwhelming the digestive system.
- Frequency: Incorporate almond milk into your diet as part of varied meals, considering it as one component of a diverse nutritional plan.
- Personalization: Adjust consumption based on individual dietary needs, considering factors such as overall calorie intake and nutritional requirements
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question; “will almond milk cause constipation?” has two sides. While it can be part of a balanced diet, moderation is crucial, and individual factors such as fiber intake and personal sensitivities must be considered or else over dose may cause constipation. Almond milk offers a lactose-free option, potentially supporting gut health, but it is essential to approach its consumption mindfully. The key lies in understanding your body’s response and incorporating almond milk into a diverse, nutritionally rich diet for optimal digestive well-being. I hope we have been able to answer your concern; “can too much almond milk cause constipation?”
Frequently Asked Questions
Can almond milk really cause constipation?
While almond milk itself is not a direct cause, excessive consumption or an imbalance in dietary fiber may contribute to digestive issues for some individuals.
How much almond milk is too much?
Moderation is key. One to two cups per day is generally considered a reasonable amount, but individual tolerance varies.
Are there any specific types of almond milk to avoid?
Opt for unsweetened varieties to minimize added sugars. Individuals with nut allergies or sensitivities should choose alternatives.
What other factors can contribute to constipation?
Dehydration, low fiber intake, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medications are common factors. A holistic approach to diet and lifestyle is crucial.
Can almond milk be a part of a constipation-relief diet?
Yes, when consumed as part of a balanced diet that includes fiber-rich foods and promotes hydration, almond milk can be a positive addition.
Is almond milk better for digestion than cow’s milk?
It depends on individual preferences and dietary needs. Almond milk is suitable for those with lactose intolerance, while cow’s milk offers its own nutritional benefits.









Leave feedback about this